Grocery Tax: Understanding The Impact On Consumers And Retailers - Grocery taxes are a hot topic, with some arguing that they are a necessary way to raise revenue and others claiming that they are a regressive tax that unfairly burdens low-income families.
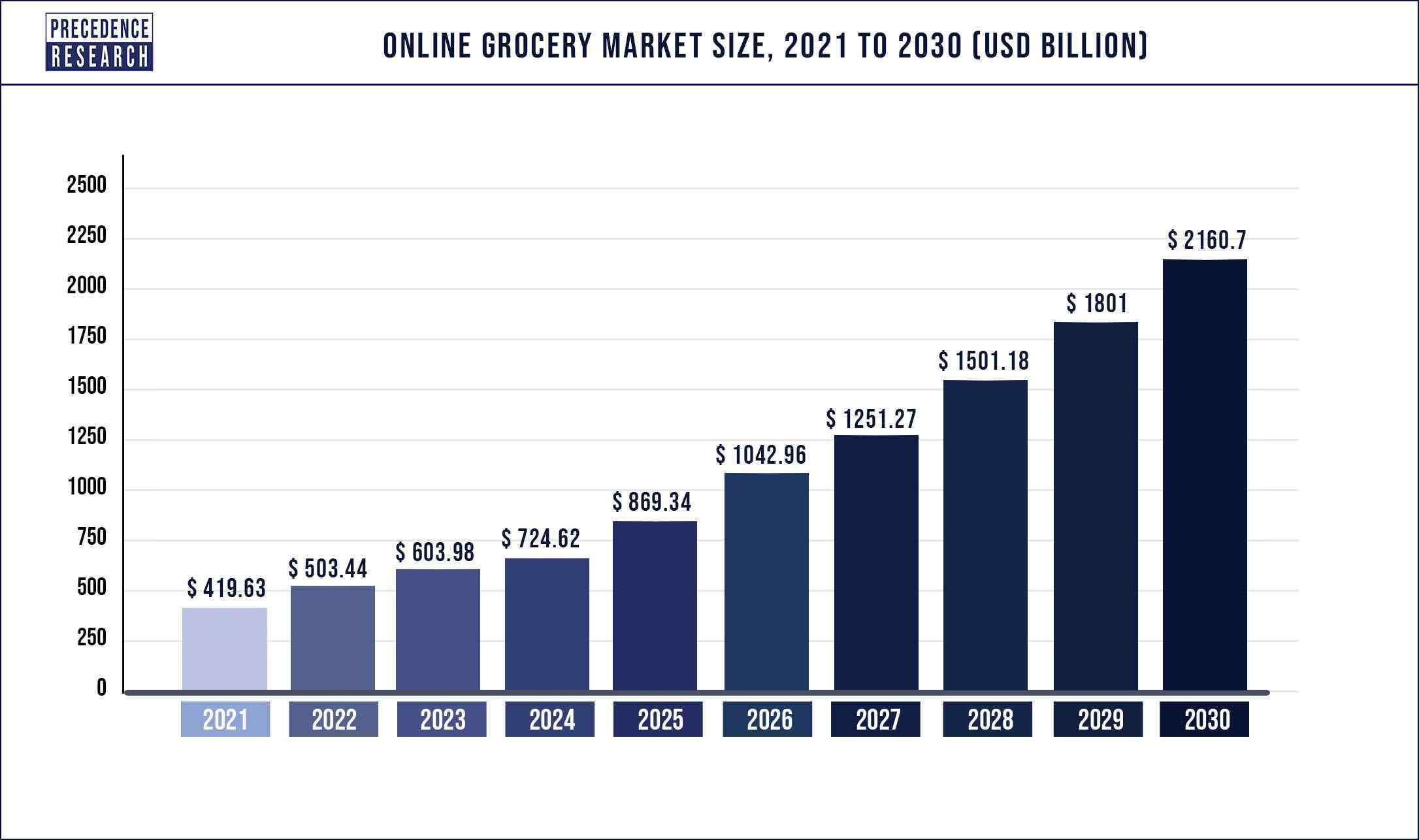
Online Grocery Market Size, Trends, Share | Report 2022-2030 - Source www.precedenceresearch.com
Editor's Notes: Grocery Tax: Understanding The Impact On Consumers And Retailers have published today date. Grocery taxes are a complex issue and understanding the impact on consumers and retailers is important, especially regressive tax impact on low-income families.
After doing some analysis, digging information, made Grocery Tax: Understanding The Impact On Consumers And Retailers we put together this Grocery Tax: Understanding The Impact On Consumers And Retailers guide to help target audience make the right decision.
Key differences or Key takeways:
Transition to main article topics:
FAQ
A grocery tax is a tax imposed on the sale of food and beverages for home consumption. Grocery Tax: Understanding The Impact On Consumers And Retailers It is a specific type of sales tax that is levied on food and beverage purchases at the point of sale.

Amid Cash Surplus, Kansas Gov. Open to Cutting Tax on Groceries to Save - Source www.newsweek.com
Question 1: What is the purpose of a grocery tax?
Answer: Grocery taxes are typically implemented to generate revenue for local or state governments. The funds raised from these taxes can be used to fund various public services, such as education, healthcare, or infrastructure projects.
Question 2: How does a grocery tax impact consumers?
Answer: Grocery taxes can increase the cost of food for consumers. This can be a significant burden for low-income households and families with limited budgets.
Question 3: How does a grocery tax impact retailers?
Answer: Grocery taxes can impact retailers by reducing their profit margins. This can lead to higher prices for consumers or lower profits for retailers.
Question 4: Are there any exemptions to grocery taxes?
Answer: Some states and localities exempt certain food items from grocery taxes. These exemptions can vary, but they often include basic necessities such as milk, bread, and produce.
Question 5: Are there any alternatives to grocery taxes?
Answer: Some states and localities have explored alternative ways to generate revenue without taxing food. These alternatives can include increasing income taxes or property taxes.
Ultimately, the decision to implement a grocery tax is a complex one that should be carefully considered. It is important to weigh the potential benefits and drawbacks of such a tax before making a decision.
Grocery taxes can be a controversial issue, with both supporters and opponents. It is important to understand the potential impact of grocery taxes on consumers and retailers before making a decision about whether or not to support such a tax.
Tips
Understanding the impact of grocery taxes on consumers and retailers is crucial for informed decision-making. The following tips provide guidance on navigating this complex issue:
Tip 1: Evaluate the Impact on Consumers
Assess how grocery taxes affect household budgets, particularly for low-income families and those with dietary restrictions. Consider the impact on essential food items versus non-essential goods.
Tip 2: Examine the Impact on Retailers
Analyze how grocery taxes influence retailer profit margins, pricing strategies, and consumer loyalty. Determine if taxes hinder competition or encourage consolidation.
Tip 3: Consider Tax Exemptions and Rebates
Explore tax exemptions and rebates on certain food items, such as healthy produce or essential staples. Evaluate the effectiveness of these measures in reducing the burden on consumers.
Tip 4: Analyze Long-Term Impacts
Assess the long-term consequences of grocery taxes on consumer spending habits, food security, and public health outcomes. Consider the cumulative effect over time.
Tip 5: Research Best Practices
Review examples of successful tax reforms or initiatives implemented in other jurisdictions. Study their approaches and lessons learned to inform decision-making.
Summary
By carefully considering these tips, policymakers, researchers, and stakeholders can gain a comprehensive understanding of the implications of grocery taxes. This knowledge empowers them to make informed decisions that balance the needs of consumers and retailers, while promoting fair and sustainable food systems.
Grocery Tax: Understanding The Impact On Consumers And Retailers
Grocery taxes, levied on the purchase of food and beverages, profoundly impact both consumers and retailers. Understanding the essential aspects of this taxation is crucial for evaluating its effects and devising appropriate policies.
- Regressive Impact: Grocery taxes disproportionately burden low-income households, who spend a larger share of their income on food.
- Inflationary Pressures: Taxes on groceries can contribute to rising food prices, exacerbating inflation and putting additional strain on consumers' budgets.
- Retailer Revenue: Grocery taxes can increase retailers' revenue, offering them a buffer against rising costs or providing funds for expansion.
- Consumer Choice: Taxes can influence consumer purchasing decisions, leading to substitutions or reduced consumption of certain food items.
- Public Health Implications: Grocery taxes aimed at unhealthy foods may encourage healthier choices, potentially reducing obesity and related health issues.
- Policy Considerations: Governments must carefully assess the trade-offs between revenue generation, social equity, and the potential impact on consumer well-being when implementing grocery taxes.
In conclusion, grocery taxes encompass a complex interplay of factors that affect consumers, retailers, and the overall food system. Balancing the need for revenue with the potential negative consequences requires policymakers to carefully consider these essential aspects and their interconnectedness.

Virginia's Grocery Tax : r/Virginia - Source www.reddit.com
Grocery Tax: Understanding The Impact On Consumers And Retailers
The implementation of a grocery tax can have significant consequences for both consumers and retailers. On the consumer side, a grocery tax increases the cost of essential goods, potentially placing a strain on household budgets. This is particularly concerning for low-income families who spend a larger proportion of their income on food. For retailers, a grocery tax can lead to reduced sales as consumers seek to minimize their tax burden by purchasing groceries from untaxed sources or by reducing their overall grocery spending.

How Filipino consumer businesses can boost performance | McKinsey - Source www.mckinsey.com
The impact of a grocery tax can vary depending on the specific tax structure. For example, a flat tax on all groceries will have a different impact than a tiered tax that exempts certain basic necessities. Additionally, the overall tax burden will depend on the local sales tax rate.
It is important to carefully consider the potential impact of a grocery tax before implementing it. Policymakers should weigh the need for additional revenue against the potential negative consequences for consumers and retailers.
Table: Impact of Grocery Tax on Consumers and Retailers
| Impact on Consumers | Impact on Retailers |
|---|---|
| Increased cost of groceries | Reduced sales |
| Strain on household budgets | Lower profits |
| Purchases from untaxed sources | Job losses |
Conclusion
The implementation of a grocery tax can have significant implications for both consumers and retailers. It is important to carefully consider the potential impact before implementing such a tax. Policymakers should weigh the need for additional revenue against the potential negative consequences for consumers and retailers.
A well-designed grocery tax can minimize the negative impact on consumers and retailers while still generating much-needed revenue. However, it is important to remember that a grocery tax is a regressive tax that disproportionately impacts low-income households.